Nasal septal defects are a common pathology in children and adults, requiring radical (surgical) treatment. This pathology is not fatal, but it is a pronounced cosmetic defect. Correction of the nasal septum (septoplasty) is performed according to strict indications.

Varieties and causes of septal defects
There are the following types of defects:
The most common causes of nasal septum deviation are:
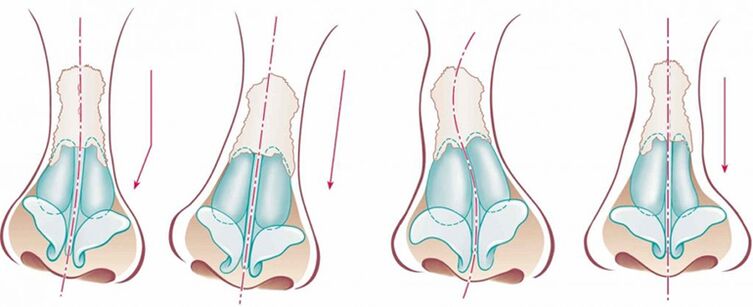
External manifestations and internal symptoms
If a person has a curved nasal septum, the following symptoms are possible:

Less commonly, symptoms such as coughing, sweating, decreased smell, tinnitus, dryness, nasality, changes in facial expressions (open mouth, change in bite) are observed.
Diagnosis of the severity of the defect
The following studies allow us to identify the defect and its severity:
In addition, analyzes (allergy tests, bacteriological examination of smears, a clinical blood test) and an inquiry are carried out.
treatment methods
Removal of the defect is only possible by surgery. The operation is called a rhinoplasty. Conservative therapy is ineffective.
Which doctors to contact
If you have symptoms of a septal defect, you should consult an otolaryngologist (otolaryngologist). You may also need to see a surgeon.

Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment aims to eliminate edema and symptoms (runny nose, congestion). Saline solutions, vasoconstrictor sprays and drops can be used. Laser therapy is often performed.
Surgical intervention (septoplasty)
Septoplasty is a surgical correction of the nasal septum. It is most often performed endoscopically without incisions using a monitor and camera. Your benefits include:
- rapid rehabilitation;
- efficiency;
- simplicity;
- minimal blood loss and trauma;
- the presence of an antiseptic effect (when using a laser).
Less commonly, the resection or septochondroprotection method is used. Before septoplasty, the degree of difficulty in nasal breathing and the patient's age are taken into account.
Indications for surgery
Indications for nose surgery are:
- difficulty breathing;
- the presence of chronic rhinitis;
- ear infection;
- severe headaches;
- pronounced cosmetic defect;
- sinusitis;
- pronounced snoring;
- regular nosebleeds.
Contraindications for the operation
Surgical correction of the nasal septum is contraindicated:
- elderly patients,
- with hemophilia (blood clotting disorder),
- severe heart disease,
- Mental Disorders, Mental Disorder
- diabetes,
- Cancer,
- severe forms of infection,
- arterial hypertension,
- during the flowering period of plants (with allergies),
- During the pregnancy,
- breastfeeding the baby.

Preparing for Septoplasty
Straightening of the nose is performed after tests (for HIV, syphilis, coagulograms), consultation with specialists (therapist, otolaryngologist, anesthesiologist), premedication and anesthesia.
The day before, it is recommended not to eat after 18 hours and to clean the intestine.
It is important to sanitize the oral cavity (to cure all diseases, including sore throat, rhinitis, pharyngitis).
For women, it is recommended to restore the correct shape of the nose 2 weeks after menstruation.
Characteristics of the postoperative period
After the nasal septum correction operation, it is necessary to:
- wear cotton tufts on the nose for 1-2 days;
- taking antibiotics for prophylactic purposes;
- observed by a doctor (a specialist should rinse the nose, clean it of scabs and blood).
Prohibitions during the rehabilitation period
After rhinoplasty, it is recommended:
- avoid high loads;
- refusing to visit baths and saunas;
- don't pick your nose;
- don't cool too much;
- exclude pressure and temperature drops (denying flights, climbing, swimming).
The effectiveness of surgical intervention
Pictures of people before and after surgery differ dramatically.
Removing the defect removes the cosmetic defect and all symptoms, making breathing easier.
Efficiency reaches 95-100%.
Complications after nasal septum correction
Correction of the nasal septum in the current stage of medical development, the operation is simple. But there can still be post-operative complications.
The consequences of the operation can be adhesions, tissue fusion, hematoma or abscess formation, infection, allergy to anesthesia, damage to the ethmoid plaque, decreased smell, perforation, blurred vision and nerve damage.




















